HYDROGEOLOGY
هیدروژئولوژی - مدل سازی و مدیریت آب زیرزمینی
HYDROGEOLOGY
هیدروژئولوژی - مدل سازی و مدیریت آب زیرزمینیMODFLOW
MODFLOW
MODFLOW is the U.S. Geological Survey modular finite-difference flow model, which is a computer code that solves the groundwater flow equation. The program is used by hydrogeologists to simulate the flow of groundwater through aquifers. The code is free software, written primarily in Fortran, and can compile and run on DOS, Windows or Unix-like operating systems.
Since its original development in the early 1980s, the USGS have released four major releases, and is now considered to be the de facto standard code for aquifer simulation. Currently, there are at least five actively developed commercial and non-commercial graphical user interfaces for MODFLOW.
Groundwater flow equation
The governing partial differential equation used in MODFLOW is:
where
- Kxx, Kyy and Kzz are the values of hydraulic conductivity along the x, y, and z coordinate axes (L/T)
- h is the potentiometric head (L)
- W is a volumetric flux per unit volume representing sources and/or sinks of water, where negative values are extractions, and positive values are injections (T−1)
- SS is the specific storage of the porous material (L−1); and
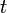 is time (T)
is time (T)
Finite difference
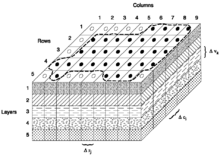
The finite difference form of the partial differential in a discretized aquifer domain (represented using rows, columns and layers) is:
where
 is the hydraulic head at cell i,j,k at time step m
is the hydraulic head at cell i,j,k at time step m- CV, CR and CC are the hydraulic conductances, or branch conductances between node i,j,k and a neighboring node
 is the sum of coefficients of head from source and sink terms
is the sum of coefficients of head from source and sink terms is the sum of constants from source and sink terms, where
is the sum of constants from source and sink terms, where  is flow out of the groundwater system (such as pumping) and
is flow out of the groundwater system (such as pumping) and  is flow in (such as injection)
is flow in (such as injection)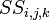 is the specific storage
is the specific storage ,
,  and
and 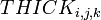 are the dimensions of cell i,j,k, which, when multiplied, represent the volume of the cell
are the dimensions of cell i,j,k, which, when multiplied, represent the volume of the cell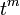 is the time at time step m
is the time at time step m
Limitations
- The water must have a constant density, dynamic viscosity (and consequently temperature) throughout the modelling domain (SEAWAT is a modified version of MODFLOW which is designed for density-dependent groundwater flow and transport)
 |
- The principle components of anisotropy of the hydraulic conductivity used in MODFLOW is displayed on the right. This tensor does not allow non-orthogonal anisotropies, as could be expected from flow in fractures. Horizontal anisotropy for an entire layer can be represented by the coefficient "TRPY" (Data Item 3 Page 153 [2].


























ایمیل شما بعد از ثبت نمایش داده نخواهد شد